Different Ways To Reduce Tax Liability
It's that time of the year when the annual tax filing ritual comes around. For many of us, this task is not exactly enjoyable, and we often want to get it over with as quickly as possible. However, in our haste, we must not overlook the importance of efficient tax filing. Mishandling this process can lead to higher tax payments and financial mismanagement. It's essential to leverage various strategies to minimize our tax liability while ensuring our financial plans stay on track to achieve our goals.
Taxation rules change frequently, so it's crucial to stay informed about the current year's updates. This helps us avoid filing inaccurate returns that could result in penalties and other issues.
Let's explore different ways to reduce your tax liability:
Investments: Under Section 80C, you can invest in specific products and receive exemptions of up to ₹1,50,000 on your gross total income. Eligible investment options include:
- Public Provident Fund (PPF)
- Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Equity Linked Savings Schemes (ELSS)
- National Saving Certificates (NSC)
- 5-year fixed deposits with banks and post offices
- Sukanya Samriddhi Account
Before investing, it's essential to understand the risks, returns, and redemption details of these products and choose based on your financial requirements and risk tolerance. For instance, while ELSS schemes offer higher return potential compared to fixed deposits, they are subject to more volatility and do not guarantee returns. Note that the Sukanya Samriddhi account is exclusively applicable for girl children.
Additionally, you can invest in government-approved pension schemes like NPS or APY to gain additional tax exemptions of up to ₹50,000 under Section 80CCD or up to ₹2,00,000 under Section 80CCE if it's the sole contribution. Keep in mind that only contributions to Tier 1 NPS accounts are eligible for these tax benefits.
Deductions: Many day-to-day expenses can be deducted from your total taxable income, effectively reducing your tax liability. These expenses include:
- Standard deduction of ₹50,000 or taxable salary (whichever is less)
- Expenses like Children’s Tuition Fees
- Premium payments for Life Insurance
- Principal repayments on housing loans
- Interest paid on home loans and education loans
- Deductions for donations to charity funds, relief funds, up to ₹50,000
- Deductions for donations to specified research associations, poverty eradication funds, or afforestation funds
- Health insurance premiums
- Expenses for a differently-abled dependent you are financially supporting. If the disability level is between 40% and 80%, you can claim a deduction of ₹75,000. For disabilities exceeding 80%, the deduction limit is ₹1,25,000.
Make sure you are aware of the specific deduction limits in each category. For instance, health insurance for self, spouse, and dependent children allows a deduction of up to ₹25,000, while medical insurance for parents under 60 years old permits a deduction of ₹25,000, and for parents above 60, it's ₹50,000.
Exemptions: Certain types of income are exempt from tax, so when calculating your taxable income, you should exclude these items. The following income sources fall under this category:
- Agricultural income
- Dividend income up to ₹1,00,000
- Interest income up to ₹10,000
- Reimbursements like House Rent Allowance (HRA) and Leave Travel Allowance (LTA)
However, please be aware that these reimbursements have limits and conditions. For example, you can only claim LTA exemption for two journeys within a block of four years. The current block spans from January 2018 to December 2021.
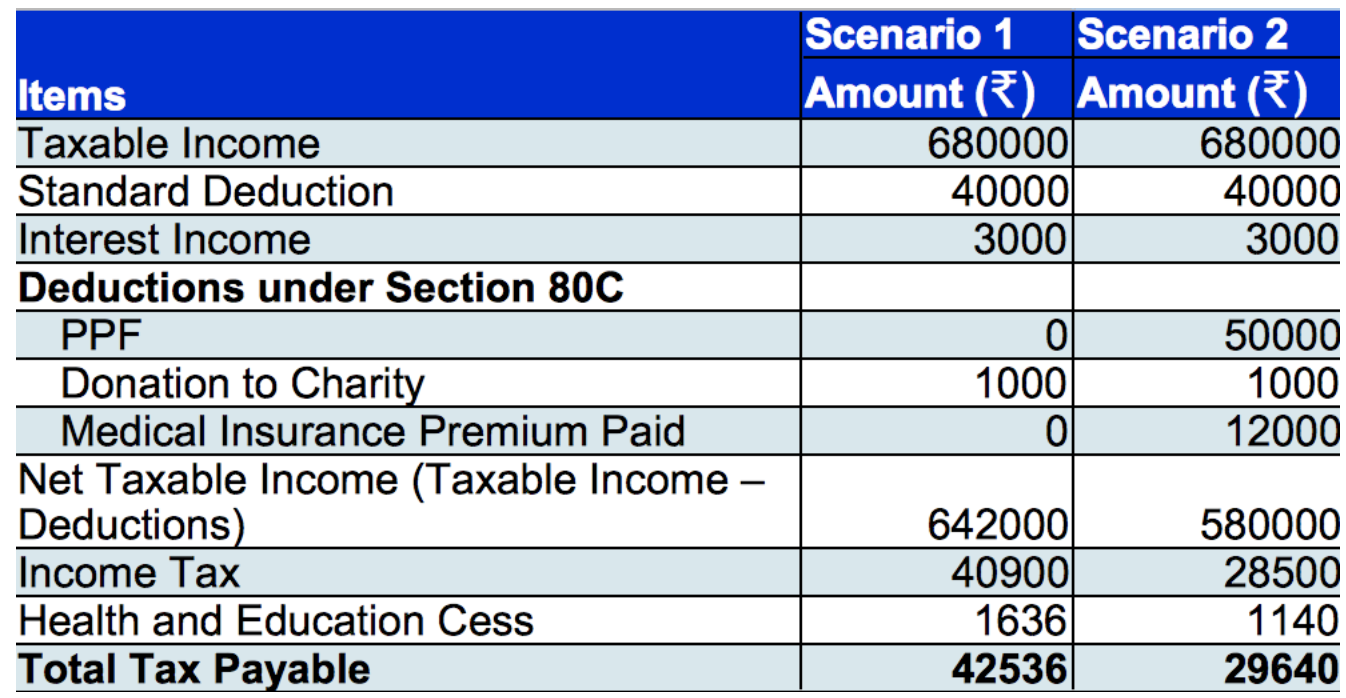
Here's an example of how to calculate the tax payable for the financial year 2018-2019:
Scenario 1: Shreya earns an annual salary of ₹6,80,000, is a resident Indian, and not a senior citizen. Her salary doesn't include HRA or LTA. In this scenario, she ends up paying a tax of ₹42,536.
Scenario 2: In this case, Shreya has invested in PPF and has taken a medical insurance policy. As a result, she reduces her tax liability and is liable to pay only ₹29,640.
As demonstrated, efficient tax planning can significantly reduce your tax liability within legal boundaries."
Vidya Kumar, Dilzer Consultants Pvt Ltd
