Plan your investments for tax savings this financial year in advance
Everyone wants to grab the opportunity, if it knocks on the door.
Section 80c is the best option not only for tax savings, but also we can create wealth in long term goals such as retirement child marriage, child education.
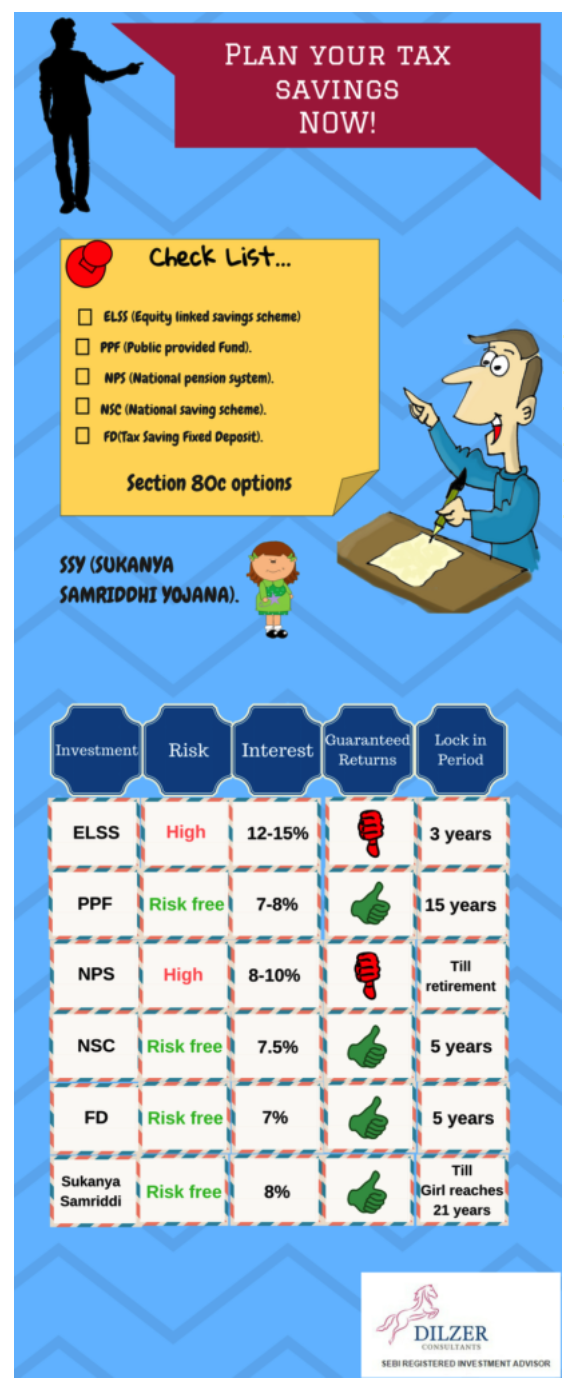
Given below are some of the options for tax savings
- ELSS (Equity Linked saving scheme).
- 2.PPF (Public provided Fund).
- NPS (National pension system).
- NSC (National saving scheme).
- FD (Tax Saving Fixed Deposit).
- SSY (SUKANYA SAMRIDDHI YOJANA).
Comparisons of popular 80C Investment Instruments.
| Investment | Risk Profile | Interest | Guaranteed Returns | Lock-in Period |
| ELSS funds | Equity-related risk | 12-15% expected | No | 3 years |
| PPF | Risk-free | 7.9.8% | Yes | 15 years |
| NPS | Equity-related | 8-10% expected | No | Till retirement |
| NSC | Risk-free | 7.6% | Yes | 5 years |
| FD | Risk-free | 7% expected | Yes | 5 years |
| SukanyaSamriddhi | Risk-free | 8.1% | Yes | Age of 21 years of girl child |
The above schemes are more often used by individuals to reduce their tax burden in the financial year..

Now we will see how these instruments will create wealth in long term.
ELSS FUNDS
ELSS is equity linked saving schemes which individuals can save tax up to 1.5 lakh 80C.
If individuals are willing to take risk, these instruments are best to get maximum returns in long term. If individual portfolio has lower equity exposure then they can choose these options.
Some benefits under ELSS:
- Tax deduction under section 80C.
- No Capital gain.
- Divided is Tax free.
- Lock-in period of 3 years.
- Long enough to withstand market Volatility.
- Better returns compared to other Instruments.
- ELSS comes under exempt-exempt-exempt category.
For creating wealth using ELSS instrument assuming a tenure of 15 year you can see the following example.
Mr. Raghu wants to save tax under 80c and to create wealth in long term with tenure of 15 years.
Invested amount =1, 50,000 per annum
Tenure = 15 years.
Expected rate of return = 12%.
Total investment amount for 15 years = 62,62,992.
Drawbacks:
Premature withdrawals are not available.
Returns are not guaranteed
PPF (Public Provident Fund):
PPF is a public provident fund scheme started at 1968 framed under PPF act.It is backed by the Government of India.
The greatest advantage of this scheme it that it cannot be attached for recovery of any debts by creditor under the court of law.
PPF account can be opened in all banks and post offices in India. Tenure of PPF is 15 years.
However, on maturity this period can be extended any number of times for a block of 5 years
Individuals can save tax under section 80C up to 1.5 lakhs.
Following is the example how individual can create wealth for 15 year period of tenure.
Mr Raghu wants to save 1.5 lakhs in PPF for a tenure of 15 years at 8.10% rate of return, how much amount will be accumulated at the end of the period ?
Invested amount =1, 50, 000 per annum
Tenure =15 years.
Rate of return = 8.1%
Amount accumulated at the end of 15 years = 44, 37, 145.
Benefits of PPF:
- Tax saving under 80c up to 1.5 lakhs.
- Interest is tax free.
- Partial loans and withdrawals are available in the ppf account for pre-defined needs.
- Continuing PPF after 15 years of primary lock in.
- 5.PPF comes under Exempt-Exempt-Exempt category.
- It can open across all the banks and post offices in India.
Disadvantage in PPF is interest rate risk, which means whenever interest rate falls, the prospective balance will earn lower interest rates.
PPF can be used as a hedging tool against equity exposure in the portfolio and for overall asset allocation.
National Saving Certificate:
The National Savings Certificate (NSC) is a popular and safe small-savings instrument that combines tax savings with guaranteed returns. This scheme is backed by the government and is available at post offices. The distribution reach of India Post has added to the popularity of this scheme and it is much sought after across all investing classes.
Benefits of national saving certificates:
- Tax saving up to 1.5 lakhs under section 80c of income tax.
- It can be keep as collateral in banks against loans.
- Premature encashment is possible after three years or in case of death of the certificate holder.
- Savings in this product are risk-free because of the government-backing.
- Individual, joint or minor through guardian accounts can be opened.
Tax implication with example:
Mr Raghu wants to invest 1.5 lakhs to save tax in National saving certificate. What are the tax implications after the maturity?
Invested amount =1.5 lakhs per annum
Tenure of the certificate = 5 years.
Rate of interest = 7.9%
Amount accumulated at the end of the tenure = 219,380
Here every year interest accumulated is taxable, if individual exceeds 1.5 lakhs under 80c .
Hence compared to other instruments it is not favourable
National Pension Scheme (NPS)
Government of India established pension fund regulatory and development authority (PFRDA) on 10th October 2003 to develop and regulate pension sector in the country.
The National Pension System (NPS) was launched on 1st January, 2004 with the objective of providing retirement income to all the citizens. NPS aims to institute pension reforms and to inculcate the habit of saving for retirement amongst the citizens.
The subscriber will be allotted a unique Permanent Retirement Account Number (PRAN). This unique account number will remain the same for the rest of subscriber’s life. This unique PRAN can be used from any location in India.
PRAN will provide access to two personal accounts:
Tier I Account: This is a non-withdraw able account meant for savings uptoretirement.
Tier II Account: This is simply a voluntary savings facility. The subscriber is free to withdraw savings from this account whenever subscriber wishes. No tax benefit is available on this account.
Tax benefits:
Presently, the tax treatment for contribution made in Tier I account is Exempted-Exempted-Taxed (EET).
| Deductibles | Maximum limit | Section |
| Mandatory deduction from salary towards retirement |
1,50,000 | 80CCD(1) |
| Voluntary contribution towards NPS by employer |
10% of basic salary | 80CCD(2) |
| Voluntary contribution towards NPS made by employer |
50,000 | 80CCD(1b) |
Withdrawal option:
At end of the tenure an individual can take annuity with 40% of corpus and remaining 60% can be withdrawn
If an individual wants to exits before the tenure, one must buy a pension product worth 80% of the corpus and remaining 20% can be withdrawn
For better understanding please see the following illustration.
Mr. Raghu’s age is 30 years he opened a NPS Tire 1 account in order to save tax and for future Retirement, annually he invested 2,00,000 in tier 1 account upto retirement 60 years.
Expected rate of return is 10%. How much amount accumulated at the end tenure?
Invested amount per annum =2, 00,000.
Expected rate of return = 10%.
Retirement age = 60 years.
Current age = 30 years.
Tenure = 30 years.
Amount accumulated at 60 years = 3,61,88,685.
At the end of the maturity the person can withdrawal 60% of corpus and remaining 40% he must buy an annuity.
Tax saving Fixed Deposits:
Fixed deposits are great financial instruments for risk-free investment. It is the most popular investment avenue in India. Fixed deposits are available under various types such as senior citizen FD, tax saving FD, FCNR deposits and so on.
Fixed deposit schemes falling under the ambit of the much-popular Section 80c of the Income Tax Act, 1961 are commonly known as tax saving fixed deposit.
Tax saver fixed deposits are simple instruments to get deductions up to Rs.1.5 lakhs per year.
Guidelines of Tax saving fixed deposits:
- Maturity: 5 Years.
- Minimum investment: Rs 100 and thereafter multiple of 100.
- Maximum investment: Rs 150,000.
- Deduction available to: individual, HUF.
- Premature withdraw: Not available.
- Loan against FD: Not available.
Please note: Interests earned on FDs are taxable.
For example Mr Raghu Invested 1.5 lakhs in a tax saving fixed deposit with rate of interest 8% with lock in period 5 years?
Invested amount =150000.
Rate of Interest = 8%.
Tenure = 5 years.
Accumulated amount at the end of tenure = 220400.
Here- interest paid by the banks is taxable every year if individual does not submit form 15g or 15H.
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana:
Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana is a government backed scheme targeted at parents of girl children. The scheme encourages parents to build for future education and marriage expenses fortheir girl child.
Key points for the Sukanya Samriddhi Yojana:
- Account can be in the name of adopted girl child.
- Two accounts are permissible for upto two girl children.
- Account can be opened until the girl is of 10 years of age.
- To open this account birth certificate of girl child is required.
- Minimum amount is 1000 and maximum 150,000 per year.
- Payment under the scheme is 14 years plus account opening year payment.
- Maturity of the account when the girl child attains age 21 years.
- It is transferable to any post office or banks with in the country.
For better understanding please go through following illustration.
Mr Raghu opened a SukanyaSamriddhiyojana account on behalf of her 6 year old daughter ,currently he is deposits 1.5 lakhs per annum, how much amount will get at time of maturity?
| Year | daughter’s age | Deposited amount | Principle+ interest at end of the year | Interest |
| 2017 | 6 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 1,62,600.00 | 8.40% |
| 2018 | 7 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 3,38,858.40 | 8.40% |
| 2019 | 8 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 5,29,922.51 | 8.40% |
| 2020 | 9 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 7,37,036.00 | 8.40% |
| 2021 | 10 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 9,61,547.02 | 8.40% |
| 2022 | 11 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 12,04,916.95 | 8.40% |
| 2023 | 12 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 14,68,729.97 | 8.40% |
| 2024 | 13 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 17,54,703.32 | 8.40% |
| 2025 | 14 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 20,64,698.05 | 8.40% |
| 2026 | 15 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 24,00,732.63 | 8.40% |
| 2027 | 16 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 27,64,993.49 | 8.40% |
| 2028 | 17 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 31,59,852.41 | 8.40% |
| 2029 | 18 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 35,87,879.57 | 8.40% |
| 2030 | 19 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 40,51,861.92 | 8.40% |
| 2031 | 20 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 45,54,817.32 | 8.40% |
| 2032 | 21 | 1,50,000 | ₹ 51,00,021.63 | 8.40% |
| Total amount | 51,00,021.63 |
Drawbacks:
- No fixed interest rate.
- Premature withdrawal not allowed.
- High lock in period.
- No online transfer facility in post office.
There are other tax saving options also available to save tax under Sec 80 C
For more details, please contact us
Krishna Chaitanya
Para Planner Dilzer Consultants Pvt Ltd
14 April 2017