Types of General Insurance
Insurance in broad terms may be described as a method of sharing financial losses of few from a common fund who are equally exposed to the same loss.
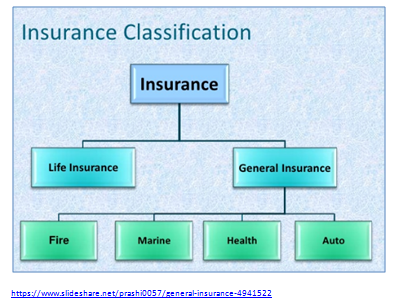
https://www.slideshare.net/prashi0057/general-insurance-4941522
Main types of general insurance are: Fire , Health, Marine, Motor Vehicle
Fire Insurance
Fire insurance is a form of property insurance which protects people from the costs incurred by fires. When a structure is covered by fire insurance, the insurance policy will pay out in the event that the structure is damaged or destroyed by fire.
Types of Fire Insurance Policies-
Specific policy: In this type of policy, the insurance company is liable to pay a sum, which may be less than the property’s real value. The insured is called to bear a part of the loss, as the actual value of the property is not considered in deciding the amount of indemnity.
Comprehensive policy: Known as “all-in-one” policy, the insurance company indemnifies the policyholder for loss arising out of fire, burglary, theft and third party risks. In this type of policy, the policyholder also gets paid for loss of profits incurred, due to fire, till the time the business remains shut. Valued policy: In this type of policy, the value of the commodity is already set and actual loss is not taken into consideration. The policy follows a standard contract of indemnity, wherein the policyholder gets paid a specific amount of indemnity, without considering the actual loss.
Floating policy: This type of policy is subject to average clause and the extent of coverage expands to different properties, belonging to the policyholder, under the same contract and one premium. The floating policy also provides protection of goods kept at two different stores. Replacement or Re-instatement policy: As per replacement or re-instatement policy, the insurance company instead of paying the policyholder the amount of indemnity in cash, replaces the damaged property/commodity with a new one.
Fire Insurance Claim Procedure
Individuals/corporate must inform insurer as early as possible , in no case later than 24 hours. Provide relevant information to the surveyor/claim representative appointed by the insurer. The surveyor then analyzes the extent/ value of loss or damage. The claim process takes anywhere between one to three weeks.
Documents Required- True copy of the policy along with schedule, Report of fire brigade, Claim Form, Photographs.
Need of Fire Insurance:
Fire insurance is important because a disaster can occur at any time. There could be many factors behind a fire, for example arson, natural elements, faulty wiring, etc. The major reason for a residential fire is unattended cooking.
Perils Covered:
Cause of Loss Fire Lightning Explosion/Implosion Aircraft damage Riot, Strike Terrorism Storm, Flood, inundation Impact damage Subsidence, landslide ,bursting or overflowing of tanks, Missile Testing Operations , Bush fire etc.
Exclusions: Loss or damage caused by war, civil war and kindered perils, Loss or damage caused by nuclear activity, Loss or damage to the stocks in cold storage caused by change in temperature, Loss or damage due to over-running of electric and/ or electronic machines
Health Insurance
Health insurance, like other forms of insurance, is a form of collectivism by means of which people collectively pool their risk, in this case the risk of incurring medical expenses.
Types of Health Insurance Plans :
Individual health plan
Family floater plan
Senior Citizens’ plan
Critical illness plan
Daily hospital cash and
Unit-linked health plan (ULHP).
Individual Health Plans : Largely, an individual health insurance plan (IHIP), or ‘mediclaim’, would cover expenses if you are hospitalised for at least 24 hours. These plans are indemnity policies, that is, they reimburse the actual expenses incurred up to the amount of the cover that you buy. Some of the expenses that are covered are room rent, doctor’s fees, anaesthetist’s fees, cost of blood and oxygen, and operation theatre charges.
Family Floater Plans :
This is a fairly new entrant in the health insurance firmament. It takes advantage of the fact that the possibility of all members of a family falling ill at the same time or within the same year is low. Under a family floater (FF) health plan, the entire sum insured can be availed by any or all members and is not restricted to one individual only as is the case in an individual health plan.
Let’s look at an example. If, a family of four has individual covers of Rs 1 lakh each. If the cost of treating one person crosses Rs 1 lakh, then the rest has to be borne by the family out of its own money. If, however, the entire family is insured for Rs 4 lakh through a floater policy, then any of the members will be covered for that amount in any year. To the extent of the annual cover, any number of members can avail the money.
Senior Citizens’ Plans:
Insurance is considered a form of long-term savings for senior citizens. This money provides financial stability and also helps them in times of need. Medical insurance enables senior citizens to pay for health checkups, emergency medical costs and long-term treatment. The income tax benefit on insurance premiums is up to Rs. 25,000 under Section 80 D of the Income Tax Act, as on March 31, 20017.
Critical Illness Plans :
A Critical Illness plan means to insure against the risk of serious illness. It will give the same security of knowing that a guaranteed cash sum will be paid if the unexpected happens and one is diagnosed with a critical illness. The purpose of a critical illness plan is to let you put aside a small regular amount now, as an insurance against all this happening.
Bajaj Allianz, in its efforts to provide a customer centric solution is offering an insurance policy to cover to some of these critical illnesses like Cancer Coronary Artery bypass surgery First Heart attack Kidney Failure Multiple sclerosis Major organ transplant Stroke Arota graft surgery Paralysis Primary Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension.
Daily Hospital Cash Expense:
Benefit is paid on per day basis after hospitalization (most plans mandate at least 48 hours of hospitalization). The pre-decided daily benefit amount is paid in full, irrespective of the actual expenses. For example, a person buys a DHC plan with a limit of Rs 2,000 per day. He gets hospitalised for 7 days and the total bill is Rs 35,000. He would be reimbursed Rs 14,000 (2,000×7). If the bill is Rs 8,000, he would still be reimbursed Rs 14,000.
Unit-linked health plan (ULHP):
All ULHPs offer one or more combination of the other benefits (for which risk premium is deducted from fund value). Also, charges such as premium allocation charge and policy administration charge are deducted from the fund value. LIC has launched Health Plus plan, a unique long term health insurance plan that combines health insurance covers for the entire family (husband, wife and the children) – Hospital Cash Benefit (HCB) and Major Surgical Benefit (MSB) along with a ULIP component (investment in the form of Units) that is specifically designed to meet domiciliary treatment (DTB) related expenses for the insured members.
Health Insurance in India:
The health insurance market in India is very limited covering about 10% of the total population. The existing schemes can be categorized as: Voluntary health insurance schemes or private-for-profit schemes; Mandatory health insurance schemes or government run schemes (namely ESIS, CGHS).Insurance offered by NGOs / community based health insurance, and Employer-based schemes
Employer based schemes:
Employers in both public and private sector offers employer based insurance schemes through their own employer. These facilities are by way of lump sum payments, reimbursement of employees’ health expenditure for out patient care and hospitalization, fixed medical allowance or covering them under the group health insurance schemes. The Railways, Defense and Security forces, Plantation sector and Mining sector run their own health services for employees and their families.
Auto Insurance
Auto insurance (also known as vehicle insurance, car insurance, or motor insurance) is insurance purchased for cars, trucks, and other vehicles. Its primary use is to provide protection against losses incurred as a result of traffic accidents and against liability that could be incurred in an accident.
Auto Insurance Coverage: Auto insurance provides property, liability and medical coverage:
Property coverage pays for damage to or theft of the car. Liability coverage pays for the legal responsibility to others for bodily injury or property damage. Medical coverage pays for the cost of treating injuries, rehabilitation and sometimes lost wages and funeral expenses
Coverage Levels: Vehicle insurance can cover some or all of the following items:
The insured party, The insured vehicle, Third parties (car and people), fire and theft in some jurisdictions coverage for injuries to persons riding in the insured vehicle is available without regard to fault in the auto accident (No Fault Auto Insurance)
Types of Auto Insurance in India:
There are different types of Auto Insurance in India : Private car insurance: It is the fastest growing sector as it is compulsory for all the new cars. The amount of premium depends on the make and value of the car, state where the car is registered and the year of manufacture. Two wheeler insurance: It covers accidental insurance for the drivers of the vehicle. The amount of premium depends on the current showroom price multiplied by the depreciation rate fixed by the Tariff Advisory Committee at the time of the beginning of policy period. Commercial vehicle insurance: It provides cover for all the vehicles which are not used for personal purposes, like the Trucks and HMVs. The amount of premium depends on the showroom price of the vehicle at the commencement of the insurance period, make of the vehicle and the place of registration of the vehicle.
What it covers?: The auto insurance generally includes: Loss or damage by accident, fire, lightning, self ignition, external explosion, burglary, housebreaking or theft, malicious act. Liability for third party injury/death, third party property and liability to paid driver. On payment of appropriate additional premium, loss/damage to electrical/electronic accessories.
Exclusions: Typically, the motor insurance plan does not provide for: Normal wear and tear or general ageing of the vehicle Mechanical/electrical breakdown. Depreciation, wear and tear of consumables like tubes and tires. Damages that occur while a person is driving with invalid driving license. Damage that occur while a person is under the influence of drugs or liquor. Damage due to a war, civil war, mutiny, or nuclear risk. Claims arising out of contractual liability. Use of vehicle other than what it is meant for. For example, if a private car is being used as a taxi and gets involved in an accident, the owner will not be able to claim damages.
Children’s Education plans
The cost of higher education is already high and rising at 10-12 per cent a year. Children’s education is one of the biggest cash outflows that families must plan for. Since the rate of education inflation is so high, you need compounding to work for you over a longer period.
A delayed start not only yields a smaller corpus but can also jeopardise other financial goals. If you start investing for your child’s education in your 40s, you are likely to fall short of the required amount.
Often, parents dip into their retirement savings to fill the gap, but this can be a risky move.
As per DSP BlackRock Investor Pulse survey , it shows that though Indians have a high propensity to save and invest, they still seek safety. Almost 52 % of the 1,500 respondents said they wanted guaranteed returns from their investments.
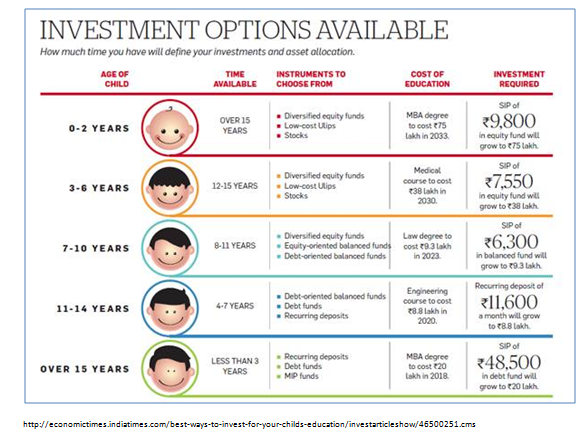
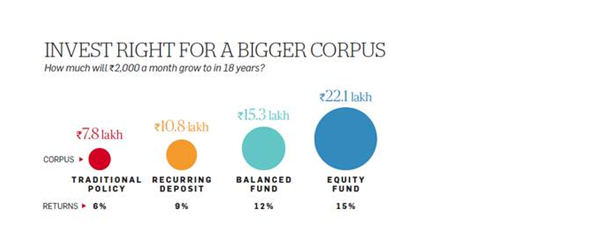
http://economictimes.indiatimes.com/best-ways-to-invest-for-your-childs-education/investarticleshow/46500251.cms
Target corpus : 1.6 crores
Some of the best investment plans for children’s education as per Investguru.com are :
Sneha Ramamurthy
Content Writer- Dilzer Consultants Pvt Ltd
